- 2012年度
- 大脳皮質の進化の謎に迫る
(2013/03/29) - 活性型ビタミンDで小胞体ストレスを緩和しよう!
(2013/03/29) - Sweat Glands Grown from Newly Identified Stem Cells
(2013/03/29) - ~筋肉の恒常性と健康は相反するものなのか?~ 筋肉においてオートファジーが存在するが故にインスリン抵抗性が存在する
(2013/03/29) - たった1つの因子の抑制で様々な細胞が神経に!?
(2013/03/28) - 乳酸菌を取り込むと、細胞も若返る?! ~"人間、またしても発酵食品のお世話になる"の巻~
(2013/03/27) - 脳腫瘍における新しい遺伝子変異~エピジェネティク
(2013/03/27) - CCR2-dependentrecruitment of macrophages by tumor-educated mesenchymal stromal cells promotes tumor development and is mimicked by TNFα
(2013/03/25) - 補体C1qはWntシグナルの活性化を介して細胞を老化させる
(2013/03/19) - Speramtogonial Stem Cell Transplantation into Rhesus Testes Regenerates Spermatogenesis Producing Functional Sperm.
(2013/03/12) - 糖尿病薬剤による抗腫瘍効果
(2013/03/12) - 難病ALSの新たな原因遺伝子の発見
(2013/03/12) - 脊髄損傷にヒートショックプロテインが有効?
(2013/03/11) - 片頭痛患者では血管内皮前駆細胞が少ない?
(2013/03/11) - 筋幹細胞の静止状態はmiRNA-489により維持される
(2013/03/11) - ストレスに弱いってどういうこと?(心の病気にかかるメカニズムの一つ、「ストレス脆弱モデル」をネズミで再現)
(2013/03/09) - 核酸医薬は実現するか~筋強直性ジストロフィー治療の可能性~
(2013/03/09) - なくならないのは技がある!
(2013/03/08) - Down症候群のiPS細胞の染色体数を修正する
(2013/03/08) - 高品質なiPS細胞作製のキーファクターZscan4の同定
(2013/03/08) - Turning off the Neuron Death Pathway
(2013/03/07) - 新しい安全な分子標識-マルチ同位体画像質量分析法-が明らかにした幹細胞の不等分裂様式
(2013/03/07) - 重度脊髄損傷後に移植した神経幹細胞が非常に長く軸索を伸長し、シナプス結合した!
(2013/03/07) - 神経系前駆細胞を元気にして水頭症を治す!?
(2013/03/05) - FUS/TLSとTDP-43 二つのALS原因遺伝子の交差点
(2013/03/01) - 貪食細胞マクロファージが造血幹細胞を優しく包み込んで自己複製能の維持に貢献していた!?
(2013/02/27) - TALENs -新遺伝子改変技術が生命科学を変える!?-
(2013/02/27) - RESTタンパク質による遺伝子発現調節 ~遺伝子発現とシナプス機能~
(2013/02/25) - 腸に住んでいるある平凡な細菌によって大腸がんは引き起こされる!
(2013/02/25) - 癌抑制遺伝子p53の変異はメバロン酸経路を活性化することで、正常な乳腺の構造を失わせる
(2013/02/25) - 樹状細胞は制御性T細胞の恒常性をコントロールすることで多発性硬化症を寛解させる
(2013/02/25) - Schwann Cell Plasticity After Spinal Cord Injury Shown by Neural Crest Lineage Tracing
(2013/02/15) - エクソソームは、癌細胞の「飛び道具」!
(2013/02/08) - 老化したニッチでは筋肉幹細胞は静止状態を保てない
(2013/01/31) - 幹細胞を使った創薬開発
(2013/01/31) - 体細胞リプログラミングにおける遺伝子発現調節の解析からわかること-single cellで見てみようの巻-
(2013/01/31) - がん幹細胞発生のかぎを握るのは誰?-ユーイング肉腫がん幹細胞の解析を通じた検証-
(2013/01/31) - 小動物用PET(Positron Emission Tomography)で、ラットの脳梗塞巣を探知することができる [18F]BMS-PET
(2013/01/31) - 脳の神経ネットワークにおけるヤングパワー!
(2013/01/18) - アストロサイトの性格はどうやって決まる?
(2013/01/18) - 幹細胞の自己複製能を制御する因子とは?
(2013/01/18) - アルデヒドが真犯人!?DNA損傷と再生不良性貧血
(2012/12/18) - HIV-2の新しい定量法
(2012/12/18) - Japanese People's Preference for Place of End-of-Life Care and Death: A Population-Based Nationwide Survey
(2012/12/18) - がん細胞の死に際
(2012/12/18) - 癌幹細胞を眠りから目覚めさせる"Coco"
(2012/12/13) - 細胞接着分子のインテグリンが血液の幹細胞の維持を制御する
(2012/12/11) - 移植された神経幹細胞は免疫系にも作用する
(2012/12/11) - 血液がん克服にむけて!~JAK2阻害剤の薬剤耐性メカニズム解明~
(2012/12/04) - 癌進展を陰で操る支配者
(2012/11/30) - 幹細胞の2つの顔を暴け!!! 未分化性維持と特異的分化との狭間で...
(2012/11/30) - 脊髄損傷後の機能回復には自発的なリハビリが効果的
(2012/11/21) - もしあなたの歯が無くなってしまった時に...
(2012/11/15) - iPS細胞から血小板をつくる
(2012/10/30) - メラノーマのエキソソームで予後予測ができる?!
(2012/10/30) - Oligodendroglia Cells Can Do Much More Than an Insulator for Neuron
(2012/09/11) - APJは、心臓肥大のデュアル受容体として作用する
(2012/09/11) - 幹細胞医療;脳梗塞治療への挑戦
(2012/09/11) - 造血幹細胞の老化と若返り
(2012/09/11) - カロリー制限が筋肉を増やす? - トレーニング界の常識に挑戦する新たな"逆説"
(2012/09/11) - 癌幹細胞は治療標的にならない!?
(2012/08/24) - iPS細胞でC型肝炎ウイルス感染のモデルをつくる
(2012/08/09) - ES細胞、iPS細胞から内耳有毛細胞への分化誘導
(2012/08/09) - 造血幹細胞を冬眠させる細胞はなんと神経系の細胞だった!
(2012/07/06) - 個別化治療への障壁 ~多重人格なガンを克服せよ~
(2012/07/06) - 栄養のバランスが新しいニューロンを作り、体重や新陳代謝をコントロールする
(2012/05/11) - 脊髄不全損傷後におこる、残存神経ネットワークの代償機能
(2012/05/11) - "スーパーPTENマウス"
(2012/04/20) - 統合失調症iPS細胞研究が臨床研究になるために
(2012/04/20) - 発癌機序における"はじめの一歩"
(2012/04/06) - iPS細胞は脊髄損傷を治せるのか?
(2012/04/06)
- 大脳皮質の進化の謎に迫る
- 2011年度
- 2010年度
ホーム > 世界の幹細胞(関連)論文紹介 > Sweat Glands Grown from Newly Ident...
Sweat Glands Grown from Newly Identified Stem Cells
論文紹介著者

Liu Ying(博士課程 1年)
GCOE RA
Department of Ophthalmology
第一著者名・掲載雑誌・号・掲載年月
Catherine P. Lu/cell 150, 136-150, July 6, 2012
文献の英文表記:著者名・論文の表題・雑誌名・巻・号・ページ・発行年(西暦)
Catherine P. Lu, Lisa Polak, Ana Sofia Rocha, H. Amalia Pasolli, Shann-Ching Chen, Neha Sharma, Cedric Blanpain, and Elaine Fuchs. Identification of Stem Cell Populations in Sweat Glands and Ducts Reveals Roles in Homeostasis and Wound Repair. CELL. 150, 136-150, July 6, 2012
論文解説
Highlights
- Populations of unipotent stem cells maintain adult homeostasis in glabrous skin
- Depending on the mode of injury, each stem cell type responds differently but unipotently
- Sweat duct basal cells and gland myoepithelial cells are multipotent when engrafted
- Sweat and mammary gland stem cells differ in transcription and tissue regeneration patterns
Sweat glands are the most common glands in the body, and they regulate body temperature to avoid hyperthermia, stroke, and death. Recently, Catherine et al. developed a strategy for the purification and molecular characterization of three different stem cell populations that constitute the complex sweat ducts and glands of the skin. The three stem cell populations respond distinctly to different types of skin injuries and to engraftments in a variety of foreign environments.
Sweat ductal and epidermal progenitors (Figure 1: in red) proliferate and repair epidermal scratch wounds; sweat gland progenitors (in blue and green) show no signs of proliferation to this type of wound, but they respond to deep glandular wounds.
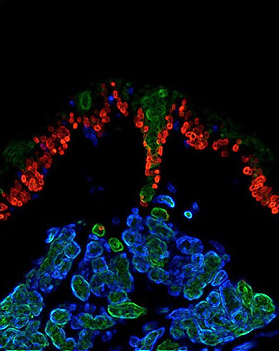
Figure 1
Using the iodine/starch-based sweat test, the authors discovered that both the luminal and myoepithelial stem cells of adult sweat glands possess regenerative potential that can be elicited in response to localized injury (Figure 2). 7 days after DT treatment, dots resurfaced, indicating that sweat gland function had been restored. These results indicate the existence of two distinct types of resident unipotent stem cells.
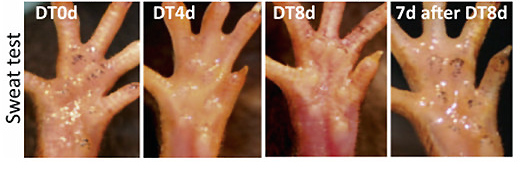
Figure 2
The authors devised a strategy to fluorescently tag and sort the different populations of ductal and glandular cells. They then used this strategy to inject each cell population into different areas of female host recipient mice to examine the cells' responses to different environments. For example, when the researchers isolated adult stem cells from these differentiated areas, they found that the cells were still able to adapt somewhat, while retaining aspects of their specialized function. When adult sweat gland stem cells were inserted into mammary fat, the cells developed into sweat glands, but when the mouse was underwent pregnancy, those same glands were able to produce milk.
Conclusions
The authors discovered that sweat glands and ducts contain stem (progenitor) cells, which can help repair damaged adult glands. Their findings can be used to explore the causes of genetic disorders that affect sweat glands, as well as to discover potential treatment modalities for these conditions. This study not only illustrates how sweat glands develop and how their cells respond to injury, but also identifies stem cells within the sweat glands and sweat ducts that have the potential to differentiate into different tissue types.
Copyright © Keio University. All rights reserved.
