- 2012年度
- 2011年度
- 新たに判明 がんの転移を促進するメカニズム
(2012/03/23) - 神経発達と加齢における5-hmCを介したエピジェネティクス
(2012/03/23) - TACEを調節するiRhom2は、リステリア菌やLPSの反応により産生されるTNFを制御している
(2012/03/09) - HIV-2って何?
(2012/03/09) - 自殺遺伝子を持ったiPS細胞
(2012/03/09) - リハビリって神経幹細胞も殖やすんです!
(2012/02/24) - 癌幹細胞を制御するHippo pathway
(2012/02/10) - 吸血鬼が若い血を好むのには根拠があった?!~若い生き血でボケ防止~
(2012/02/10) - 癌幹細胞を特異的に標的とした治療法を開発できる可能性!?
(2012/01/27) - 骨の再生には、本来体を守る役割を持つはずのサイトカインは邪魔になる!?
(2012/01/27) - 骨格筋の老化は防げる?
(2012/01/13) - 意外に他力本願???他者の掘ったトンネルを行く癌細胞
(2012/01/13) - 新しいRNA間コミュニケーションのカタチ@筋肉
(2011/12/23) - 精子形成に必須なタンパク質Miwiによるトランスポゾンの発現抑制
(2011/12/23) - Dying well with dementia
(2011/12/09) - Recent insights into the epigenetic regulation of the hair follicle bulge stem cells
(2011/12/09) - ヒトiPS細胞から誘導した神経幹細胞における脳梗塞に対する移植治療の可能性
(2011/11/25) - 体細胞の再プログラム化を阻む"小さなRNA: miR-34"
(2011/11/25) - 薬剤性過敏症症候群 - DIHSがつなぐ薬疹とウイルスとの関連性
(2011/11/11) - 線維芽細胞より作製したドパミン作動性ニューロンは生体内において機能的であるのか?
(2011/11/11) - 終末分化した肝細胞から機能的な神経細胞への直接的な系統転換
(2011/10/28) - Nerves and T Cells Connect
(2011/10/28) - Rapid and robust generation of functional oligodendrocyte progenitor cells
(2011/10/28) - 脂肪細胞が発毛を促進する!?
(2011/10/14) - ADAM13はClass B Ephrinsの分解とWntシグナルの調節により頭部神経冠を誘導する
(2011/10/14) - 多能性の維持に働くchromatin remodeling複合体esBAF
(2011/09/30) - 造血幹細胞の維持にはp57が重要である
(2011/09/30) - IGF-II : 記憶力がよくなる分子!?
(2011/09/16) - 固形腫瘍に存在する間葉系幹細胞は癌幹細胞を増加させる
(2011/09/16) - 小腸は抑制性Th17細胞の宝庫
(2011/09/02) - 細胞周期を制御する新規noncoding RNA
(2011/09/02) - Sema3A play an important role in remyelination failure in multiple sclerosis
(2011/08/19) - Drosophila Sex lethal Gene initiates Female Development in Germline Progenitors
(2011/08/19) - Wnt signaling is a key pathway for regulation of Melanocyte stem cells.
(2011/08/05) - A step closer to understanding the heart
(2011/08/05) - 神経再生を阻む「死」のシグナル
(2011/07/25) - テロメラーゼの再活性化によりマウスの組織老化が回復する
(2011/07/25) - 新遺伝子「Glis1」により、安全なiPS細胞を高効率に作製可能
(2011/07/08) - 幹細胞の"状態"をつくりだす細胞外環境
(2011/07/08) - 毛包幹細胞、色素幹細胞を維持
(2011/06/24) - BCL6を標的とした白血病の新たな治療戦略
(2011/06/24) - 自家移植におけるiPS細胞の免疫応答について
(2011/06/03) - ヒト疾患iPS細胞のウィルソン病への応用
(2011/06/03) - FOP(進行性骨化性線維異形成症)の異所性骨化部の起源は?
(2011/04/22) - 非対称分裂がNotchシグナルの活性化を介して皮膚の分化を促進する
(2011/04/22) - ショウジョウバエの腸管幹細胞の増殖は活性酸素により制御される
(2011/04/22) - 線維芽細胞からの直接的なエピブラストステムセルの誘導
(2011/04/08) - 抗リウマチ薬DHODH阻害剤はメラノーマの進展を抑える
(2011/04/08) - 癌再発の指標になる幹細胞
(2011/04/08)
- 新たに判明 がんの転移を促進するメカニズム
- 2010年度
ホーム > 世界の幹細胞(関連)論文紹介 > Sema3A play an important role in re...
Sema3A play an important role in remyelination failure in multiple sclerosis
論文紹介著者

Liang Zhang(博士課程 2年)
GCOE RA
Department of rehabilitation medicine
第一著者名・掲載雑誌・号・掲載年月
Yasir A. Syed/J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 9;31(10):3719-28.
文献の英文表記:著者名・論文の表題・雑誌名・巻・号・ページ・発行年(西暦)
Syed YA, Hand E, Mobius W, Zhao C, Hofer M, Nave KA, Kotter MR. Inhibition of CNS remyelination by the presence of semaphorin 3A. J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 9;31(10):3719-28.
論文解説
Introduction
Multiple sclerosis (abbreviated MS) is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths*1 around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms. A person with MS can suffer almost any neurological symptom or sign, including changes in sensation, muscle weakness, clonus, muscle spasms, or difficulty in moving; difficulties with coordination and balance; problems in speech or swallowing, visual problems, fatigue, acute or chronic pain, and bladder and bowel difficulties.
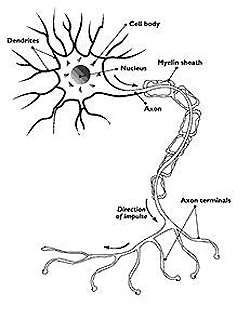
Oligodendrocyto precursor cells are the major remyelinating players in the adult CNS. Recently, failure of oligodendrocyte precursor cell (OPC)*2 differentiation has been recognized as a reason of demyelination diseases such as MS, although the mechanism of which contribute to this failure has not been elucidated clearly. Semaphorin3A, which is a repulsive guidance cue for neuronal and glial cells in CNS, expressed in active MS lesions. However, the roles of Sema3A expression in MS remain unclear.
Summary
To identify whether Sema3A inhibits CNS remyelination and play an important role in the differentiation block occurring in MS lesions, authors administrated Sema3A into demyelinating lesions in rat CNS. This work showed that only the presence of Sema3A resulted in a reduction of differentiatin O4-positive OPCs, which means sema3A selectively inhibits the differentiation of OPCs into oligodendrocytes. This inhibition is dose-dependent and reversible. Sema3A does not alter the macrophage*4 response and the presence of OPCs in demyelinated lesions. It only arrests OPCs at a premyelinating state.
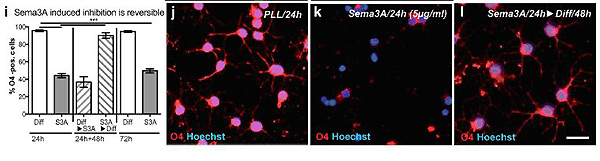
The inhibition of OPC differentiation by Sema3A is reversible. Cells inhibited as long as Sema3A was present in the medium(72h).However, this outcome was reversed following replacement with non-Sema3A containing medium
Conclusion
Extrinsic environment factors, such as Semaphorin3A, are implied play an important role in the differentiation block occurring in MS lesions. It can be regards as regulators and inhibitors in OPC migration and differentiation. This study opened new avenues to understand remyelination failure and promote repair in MS. Thus it provided a new target for the treatment of clinical demyelinating cases.
用語解説
- *1 Myelin sheath is a dielectric material that forms a layer around the axon of a neuron. It is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system.
- *2 Oligodendrocyte precursor cell (OPC) in nervous tissue cells precede oligodendrocytes, and may also be able to generate neurons and astrocytes. The principal function of oligodendrocytes is to provide support to axons and to produce the Myelin sheath in CNS.
- *3 Semaphorin3A is one of the semaphorins which are large family of guidance molecules. It is produced by meningeal fibroblasts of the gilal scar and is the best studied semaphorins in spinal cord injury. Semaphorins not only serve as neurite repulsion and attraction, but also play important roles in such as immune modulation, organogenesis, angiogenesis, neuronal apoptosis and neoplastic transformation.
- *4 Macrophages play an important role in the process of remyelination.
Copyright © Keio University. All rights reserved.
