- 2012年度
- 2011年度
- 新たに判明 がんの転移を促進するメカニズム
(2012/03/23) - 神経発達と加齢における5-hmCを介したエピジェネティクス
(2012/03/23) - TACEを調節するiRhom2は、リステリア菌やLPSの反応により産生されるTNFを制御している
(2012/03/09) - HIV-2って何?
(2012/03/09) - 自殺遺伝子を持ったiPS細胞
(2012/03/09) - リハビリって神経幹細胞も殖やすんです!
(2012/02/24) - 癌幹細胞を制御するHippo pathway
(2012/02/10) - 吸血鬼が若い血を好むのには根拠があった?!~若い生き血でボケ防止~
(2012/02/10) - 癌幹細胞を特異的に標的とした治療法を開発できる可能性!?
(2012/01/27) - 骨の再生には、本来体を守る役割を持つはずのサイトカインは邪魔になる!?
(2012/01/27) - 骨格筋の老化は防げる?
(2012/01/13) - 意外に他力本願???他者の掘ったトンネルを行く癌細胞
(2012/01/13) - 新しいRNA間コミュニケーションのカタチ@筋肉
(2011/12/23) - 精子形成に必須なタンパク質Miwiによるトランスポゾンの発現抑制
(2011/12/23) - Dying well with dementia
(2011/12/09) - Recent insights into the epigenetic regulation of the hair follicle bulge stem cells
(2011/12/09) - ヒトiPS細胞から誘導した神経幹細胞における脳梗塞に対する移植治療の可能性
(2011/11/25) - 体細胞の再プログラム化を阻む"小さなRNA: miR-34"
(2011/11/25) - 薬剤性過敏症症候群 - DIHSがつなぐ薬疹とウイルスとの関連性
(2011/11/11) - 線維芽細胞より作製したドパミン作動性ニューロンは生体内において機能的であるのか?
(2011/11/11) - 終末分化した肝細胞から機能的な神経細胞への直接的な系統転換
(2011/10/28) - Nerves and T Cells Connect
(2011/10/28) - Rapid and robust generation of functional oligodendrocyte progenitor cells
(2011/10/28) - 脂肪細胞が発毛を促進する!?
(2011/10/14) - ADAM13はClass B Ephrinsの分解とWntシグナルの調節により頭部神経冠を誘導する
(2011/10/14) - 多能性の維持に働くchromatin remodeling複合体esBAF
(2011/09/30) - 造血幹細胞の維持にはp57が重要である
(2011/09/30) - IGF-II : 記憶力がよくなる分子!?
(2011/09/16) - 固形腫瘍に存在する間葉系幹細胞は癌幹細胞を増加させる
(2011/09/16) - 小腸は抑制性Th17細胞の宝庫
(2011/09/02) - 細胞周期を制御する新規noncoding RNA
(2011/09/02) - Sema3A play an important role in remyelination failure in multiple sclerosis
(2011/08/19) - Drosophila Sex lethal Gene initiates Female Development in Germline Progenitors
(2011/08/19) - Wnt signaling is a key pathway for regulation of Melanocyte stem cells.
(2011/08/05) - A step closer to understanding the heart
(2011/08/05) - 神経再生を阻む「死」のシグナル
(2011/07/25) - テロメラーゼの再活性化によりマウスの組織老化が回復する
(2011/07/25) - 新遺伝子「Glis1」により、安全なiPS細胞を高効率に作製可能
(2011/07/08) - 幹細胞の"状態"をつくりだす細胞外環境
(2011/07/08) - 毛包幹細胞、色素幹細胞を維持
(2011/06/24) - BCL6を標的とした白血病の新たな治療戦略
(2011/06/24) - 自家移植におけるiPS細胞の免疫応答について
(2011/06/03) - ヒト疾患iPS細胞のウィルソン病への応用
(2011/06/03) - FOP(進行性骨化性線維異形成症)の異所性骨化部の起源は?
(2011/04/22) - 非対称分裂がNotchシグナルの活性化を介して皮膚の分化を促進する
(2011/04/22) - ショウジョウバエの腸管幹細胞の増殖は活性酸素により制御される
(2011/04/22) - 線維芽細胞からの直接的なエピブラストステムセルの誘導
(2011/04/08) - 抗リウマチ薬DHODH阻害剤はメラノーマの進展を抑える
(2011/04/08) - 癌再発の指標になる幹細胞
(2011/04/08)
- 新たに判明 がんの転移を促進するメカニズム
- 2010年度
ホーム > 世界の幹細胞(関連)論文紹介 > Wnt signaling is a key pathway for ...
Wnt signaling is a key pathway for regulation of Melanocyte stem cells.
論文紹介著者

Marwah Adly Saleh(博士課程 4年)
GCOE RA
Department of Dermatology
第一著者名・掲載雑誌・号・掲載年月
Piul Rabbani and Makoto Takeo/Cell 145, 941-955, June 10, 2011
文献の英文表記:著者名・論文の表題・雑誌名・巻・号・ページ・発行年(西暦)
Piul Rabbani, Makoto Takeo, WeiChin Chou, Peggy Myung, Marcus Bosenberg, Lynda Chin, M. Mark Taketo, Mayumi Ito
Coordinated Activation of Wnt in Epithelial and Melanocyte Stem Cells Initiates Pigmented Hair Regeneration
Cell 145, 941-955, June 10, 2011
論文解説
Introduction
Successful regeneration of a functional organ relies on the organized and timely orchestration of molecular events among distinct stem/progenitor cell populations. The mammalian hair follicle (HF) contains epithelial stem cells (EpSCs) which express Keratin 15 and melanocytes stem cells (McSCs) which are responsible for the hair pigmentation. These two distinct cell populations act in concert to regenerate pigmented hair with each hair cycle. The hair cycle is composed of growth phase (anagen) and rest phase (telogen).
The molecular mechanisms that regulate EpSCs have been thoroughly studied. Wnt1/β-catenin2 signaling proved essential for EpSCs proliferation and differentiation. In contrast to EpSCs, the molecular mechanisms that regulate McSCs remain mostly unknown.
Aim of the work
To determine how Melanocyte stem cells (McSCs) and epithelial stem cells (EpSCs) become activated to proliferate and differentiate in a synchronized manner to regenerate a hair follicle.
Summary
This work showed that Wnt signaling1 is essential for McSCs differentiation and hair pigmentation. On the other hand, forced activation of Wnt signaling in McSCs results in premature differentiation of McSCs and accelerated McSCs exhaustion which leads to McSCs loss. Therefore Wnt suppression is necessary to maintain McSCs in an undifferentiated state.
The lack of β-catenin2 in EpSCs not only arrested EpSC proliferation, but also blocked McSC proliferation. Furthermore, a specific gene modulation of gene expression in EpSCs altered the behavior of McSCs. Wnt signaling in EpSCs stimulates expansion of melanocytes. This is mediated by Endothelin3 receptor B signaling. This suggests that EpSCs not only serves as the source of epithelial components of the follicle, but also regulate proliferation and differentiation of McSCs which in turn provide pigment to the epithelial cells during HF formation.
The coordinated activation of the two stem cells involving Wnt signaling may occur in the secondary hair germ.
Conclusion
The study demonstrated that Wnt signaling is a key pathway for both intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of McSCs in their niche. Furthermore, there may be other signaling pathways that activate EpSCs and influence McSCs and serve as additional means of communication between the two cell types.
The regulation of Wnt signaling in McScs may offer strategies to preserve McScs which exhaust during aging as a result of inappropriate differentiation.
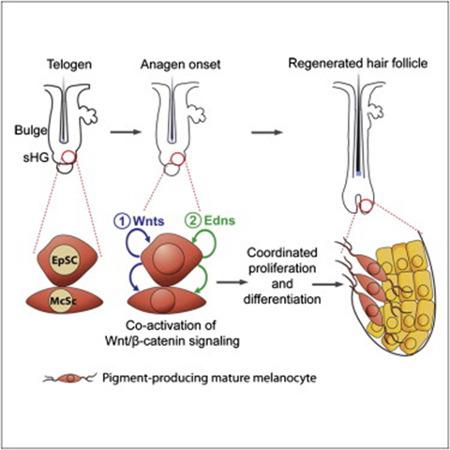
EpSCs express Wnts that activate Wnt signaling in McSCs and EpSCs at anagen onset. Similar to EpSCs, Wnt activation in McSCs commits them to differentiation. Forced Wnt activation in epithelial cells induces their endothelin upregulation. Wnt activated EpSCs express endothelins that promote melanocyte proliferation (Rabbani et., al., 2011).
用語解説
- *1 Wnt signaling is a network of proteins that are involved in physiological processes.
- *2 β-catenin is a key downstream mediator of Wnt signaling.
- *3 Endothelins are signaling peptides essential for melanocyte development.
Copyright © Keio University. All rights reserved.
