HOME > Education and Research Center for Stem Cell Medicine

GCOE Flow Cytometry Core Facility
 Leader : Yumi Matsuzaki
Leader : Yumi Matsuzaki
With the full support of the COE program "Basic Study and Clinical Application of the Human Stem Cell Biology and Immunology", in 2004 our facility set up a flow cytometry core facility and began operations with the aim of providing cell analysis and isolation research assistance. A resident staff manages all of the tasks required to utilize FCM, including maintenance, stocking the required reagents, and operating the equipment, etc. Perhaps because of the ease of using this facility, since users need only prepare samples and bring them, it has become a popular facility with a total annual utilization time of more than 5000 hours, and it is continuing to provide its services since the transition to a GCOE.
Moreover, many of the users of this facility are from outside Keio University, and it is the process of becoming an open facility available to anyone.
For more information, please consult our home page. http://keio.cytometry.jp

GCOE Keio University Vector Processing Center: KVPC
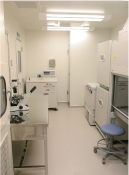


 To develop innovative therapies, such as cellular therapy and gene therapy for regenerative medical treatment and also immunotherapy based on translational research, a facility where cells and molecules for clinical use can be produced under highly controlled quality and safety conditions, is required. Clinical-grade materials should be produced under management and quality control standards that meet the requirements of GMP (good manufacturing practice) according to various laws and guidelines.
To develop innovative therapies, such as cellular therapy and gene therapy for regenerative medical treatment and also immunotherapy based on translational research, a facility where cells and molecules for clinical use can be produced under highly controlled quality and safety conditions, is required. Clinical-grade materials should be produced under management and quality control standards that meet the requirements of GMP (good manufacturing practice) according to various laws and guidelines.
Keio University School of Medicine has established the Keio University Vector Processing Center (KVPC), where clinical-grade materials are prepared under the direction of a KVPC committee. KVPC has various manuals for the operation of KVPC facilities complying with GMP for investigational new drugs (i-GMP). At KVPC, there are two P2 incubation compartments with class 10,000 level cleanliness (the number of existing 0.5-micron or larger particles in an approx. 30 cm square area: 24 hours monitoring and recording), and two different projects can be simultaneously undertaken. Room temperature, pressure, humidity and the operation status of HEPA filters are automatically controlled and recorded continuously and the operation status of equipments installed at the facilities (BHC, CO2 gas incubators, centrifuges, autoclaves, refrigerators, ultra low temperature cell storage equipment (-196℃, -150℃ and -80℃) is constantly monitored and recorded as well. The KVPC has a two-dimensional bar code system for sample management. The KVPC facility is always kept clean by daily cleaning and periodic extensive sanitation, and by monitoring of the environment by measurement of airborne particles and bacteria. The production process and management are monitored by camera monitoring for the quality control and safety of workers.
KVPC previously produced a Master Cell Bank of helper cells for the production of Herpes Simplex virus for clinical use under GMP standards. As one of the projects in the G-COE program, development of a cellular therapy for regenerative medical treatment, "multilayered corneal epithelial sheet isolated and cultured from human corneal limbic epithelium", is currently in progress, with the approval of the University IRB (institutional review board) and the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Based on the extensive experience of these operations, we expect the KVPC to become further well-established in the near future for the processing of iPS cells and ES cells, which require more stringent quality standards.
GCOE Keio University Small Fish Center : KSFC
Advantages of the Zebrafish and Medaka fish system



 It is the combination of excellent embryology and the possibilities of genetic manipulation that make the fish one of the most important vertebrate model for biological research. New methodologies and in-vivo systems need to be integrated with classical cell-biological methods to test specific hypotheses. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) research is bridging the gap between cell and developmental biology. Zebrafish and Medaka fish are small, easy to grow and sexually reproductive within three months after fertilization, when a healthy pair can provide more than two hundred embryos per week. Most organs are formed and function within the first five days of development. Embryos are also particularly well suited to cell-biological studies because they develop externally and are essentially transparent.
It is the combination of excellent embryology and the possibilities of genetic manipulation that make the fish one of the most important vertebrate model for biological research. New methodologies and in-vivo systems need to be integrated with classical cell-biological methods to test specific hypotheses. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) research is bridging the gap between cell and developmental biology. Zebrafish and Medaka fish are small, easy to grow and sexually reproductive within three months after fertilization, when a healthy pair can provide more than two hundred embryos per week. Most organs are formed and function within the first five days of development. Embryos are also particularly well suited to cell-biological studies because they develop externally and are essentially transparent.
These characteristics enable non-invasive experimental manipulations combined with live imaging of cell behavior, an attractive system with which to study dynamic processes. Furthermore, most of the organs are small enough to be mounted and imaged as a whole, enabling 3D reconstruction of entire organs. The increasing popularity of the system is also partly due to its amenability to forward and reverse genetics. The function of any given gene can be easily and rapidly assessed during the first few days of fish development by injecting Morpholino antisense oligonucleotides. Looking into conduct of a mutagenesis screen for mutants that disrupt a biological process is, however, the most straight forward and productive approach to identify crucial players in an unbiased manner. Even small laboratories can conduct reasonably-sized screens for new mutations, and the cost of a fish facility necessary to support such research is significantly lower than that for mice. The recent generation of transgenic lines carrying fluorescent protein enables the identification of mutations affecting internal organs or a very specific aspect of development.
Fish models are also becoming available for studies of the immune system and cancer. The medical relevance of the fish system is, however, most prominently manifested in the study of cardiovascular development. Fish is particularly well suited to the study heart development. Embryos are small enough to survive during the first days of development even in the total absence of circulation. The embryos receive enough oxygen through passive diffusion and are therefore not dependent on a functional heart. The advantage is that cardiac-specific phenotypes and later aspects of cardiovascular development, in particular, can be studied independently, without any deleterious secondary effects. It is becoming increasingly evident that numerous biological mechanisms of development and disease can be easily studied in the fish and that the results obtained can be extrapolated to other model organisms and humans.
Small-animal imaging has been necessary for in vivo experimental medicine, as for this GCOE.
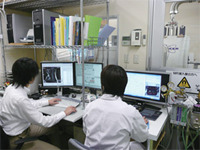
 Our role and goal in this program is to primarily develop an optimal imaging strategy for morphological and functional analysis of the central nervous systems of small animals. We are in collaboration with Central Institute for Experimental Animals, where a 7T MRI unit has been in operation since 2004. So far, we have obtained high-quality images by optimization of MRI protocols, development of animal holders and control of the physiological states. We are currently working on the development of imaging analysis, an MRI coil, and comprehensive animal monitoring for more advanced imaging. For details, please visit the following website: http//gcoe-stemcell.keio.ac.jp/center/index.html "Imaging analysis of the central nerve system of small animals"
Our role and goal in this program is to primarily develop an optimal imaging strategy for morphological and functional analysis of the central nervous systems of small animals. We are in collaboration with Central Institute for Experimental Animals, where a 7T MRI unit has been in operation since 2004. So far, we have obtained high-quality images by optimization of MRI protocols, development of animal holders and control of the physiological states. We are currently working on the development of imaging analysis, an MRI coil, and comprehensive animal monitoring for more advanced imaging. For details, please visit the following website: http//gcoe-stemcell.keio.ac.jp/center/index.html "Imaging analysis of the central nerve system of small animals"
 |
 |
GCOE Shinanomachi Campus Animal Database (SCAD)

 The SCAD is a database resource for the laboratory mouse maintained on the Keio University Shinanomachi campus, where the G-COE program is mainly conducted. The database was constructed in 2005 during 21COE, and is currently collecting information about wild-type, transgenic, knockout and knock-in mice. These mice include commonly used mice such as those expressing Cre recombinase in a tissue specific manner, and reporter mice expressing green or red fluorescent proteins (GFP, RFP) under certain conditions. The SCAD is searchable, for example, by names of mice (both official and conventional), genetic background, types of genetic manipulation, names of genes manipulated, phenotypes, names of research groups, and location of mice. Obtaining mice from overseas or outside the campus is often time consuming and expensive. The SCAD is useful to avoid redundant efforts to obtain mice without knowing that the mice are already in the campus. Not only facilitating efficient transfer of these animals (with permission of the developer), the SCAD help integrate information on these mice including the method of genotyping and the map of the genetic locus. To this end, the database is equipped with uploading function among other features. In the new framework of G-COE, the SCAD is expected to grow to provide researchers with a reliable tool for searching experimental animals in the campus and beyond.
The SCAD is a database resource for the laboratory mouse maintained on the Keio University Shinanomachi campus, where the G-COE program is mainly conducted. The database was constructed in 2005 during 21COE, and is currently collecting information about wild-type, transgenic, knockout and knock-in mice. These mice include commonly used mice such as those expressing Cre recombinase in a tissue specific manner, and reporter mice expressing green or red fluorescent proteins (GFP, RFP) under certain conditions. The SCAD is searchable, for example, by names of mice (both official and conventional), genetic background, types of genetic manipulation, names of genes manipulated, phenotypes, names of research groups, and location of mice. Obtaining mice from overseas or outside the campus is often time consuming and expensive. The SCAD is useful to avoid redundant efforts to obtain mice without knowing that the mice are already in the campus. Not only facilitating efficient transfer of these animals (with permission of the developer), the SCAD help integrate information on these mice including the method of genotyping and the map of the genetic locus. To this end, the database is equipped with uploading function among other features. In the new framework of G-COE, the SCAD is expected to grow to provide researchers with a reliable tool for searching experimental animals in the campus and beyond.
GCOE Liaison Center for Graduate School Education:GCOE-LICE

 The mission of GCOE-LICE is to select and arrange good lectures and seminars for GCOE graduate students, and to guide these students towards gaining profound knowledge and technological expertise in the area of stem cell research. The selected lectures would cover a wide range of topics related to stem cells, from basic developmental biology to current knowledge of regenerative medicine and cancer stem cells. Seminars presented by top scientists from inside and outside the country will also be included in the curriculum. GCOE-LICE has the responsibility of transmitting important information to the GCOE student in a timely manner.
The mission of GCOE-LICE is to select and arrange good lectures and seminars for GCOE graduate students, and to guide these students towards gaining profound knowledge and technological expertise in the area of stem cell research. The selected lectures would cover a wide range of topics related to stem cells, from basic developmental biology to current knowledge of regenerative medicine and cancer stem cells. Seminars presented by top scientists from inside and outside the country will also be included in the curriculum. GCOE-LICE has the responsibility of transmitting important information to the GCOE student in a timely manner.
GCOE-LICE設定による2009年度幹細胞レクチャーコース(1年次必修)
 1年次グローバルCOE RAは大学院の副科目として「幹細胞医学(担当教官 岡野栄之・佐谷秀行)」を履修して頂きます。この「幹細胞医学」という科目では、以下に述べる幹細胞に関する基礎的および最新の情報に関するレクチャーを聴講することで単位が与えられます。
1年次グローバルCOE RAは大学院の副科目として「幹細胞医学(担当教官 岡野栄之・佐谷秀行)」を履修して頂きます。この「幹細胞医学」という科目では、以下に述べる幹細胞に関する基礎的および最新の情報に関するレクチャーを聴講することで単位が与えられます。
- 医学部学生(2年生)を対象に開講される「分子細胞生物学Ⅱ(MCBⅡ)」の講義は、発生・再生に関与する多くの分野をカバーしています。15枠の講義を幹細胞レクチャーコースの講義として指定し、そのうち5枠を必ず聴講して頂くこととします。
- GCOE指定セミナー・特別講義・特別実習への出席
GCOE STEMCELL SEMINAR
GCOE指定大学院特別講義(著名講師による発生・再生研究者による講義)
GCOE特別実習(パッチクランプ法実習・セルソーター法実習)
などの開催をあらかじめ通知。1年次RAはこれらの指定セミナー・特別講義・特別実習に単位取得の最低条件として計5回以上出席して頂きます。
以上1.と2.の両方の条件を満たすことで幹細胞医学の単位を授与いたします。
Copyright © Keio University. All rights reserved.
